Step-by-Step: Three Essential APIs to Interact With LLMs
With 3 exercises: Build a simple chatbot (Lovable + Chat Completions API), a chatbot with file search (Lovable + Response API), and a chatbot that can browse the web (Replit + Responses API).
Hey, Paweł here.
I’m adding more content to the C10. LLM Systems Practitioner PM of our AI PM Learning Program, so that we can learn AI PM by doing.
Soon, the program will be converted into a set of self-paced courses. After submitting the exercises (individual or as a group), you will receive a digital certificate for each module.
In this post, we discuss:
Three Essential APIs to Interact With LLMs
Exercise 1: Build a Simple Chatbot: Lovable and Chat Completions API
🔒Example: Build a Chatbot That Can Search PDFs: Lovable and Threads API
Phase 1: Without streaming
Phase 2: With streaming
🔒Exercise 2: Build and Publish a Chatbot With Lovable + Responses API:
Phase 1: Without streaming
Phase 2: With streaming
🔒Exercise 3: Build a Chatbot That Can Search PDFs, Browse Web, or Use MCP: Replit and Responses API
Implementing a chatbot that can search PDFs with Replit
How to add Web Search or an MCP server (if we wanted)
Before we continue, you might have missed:
Consider subscribing and upgrading your account for the full experience:
Three Essential APIs to Interact With LLMs
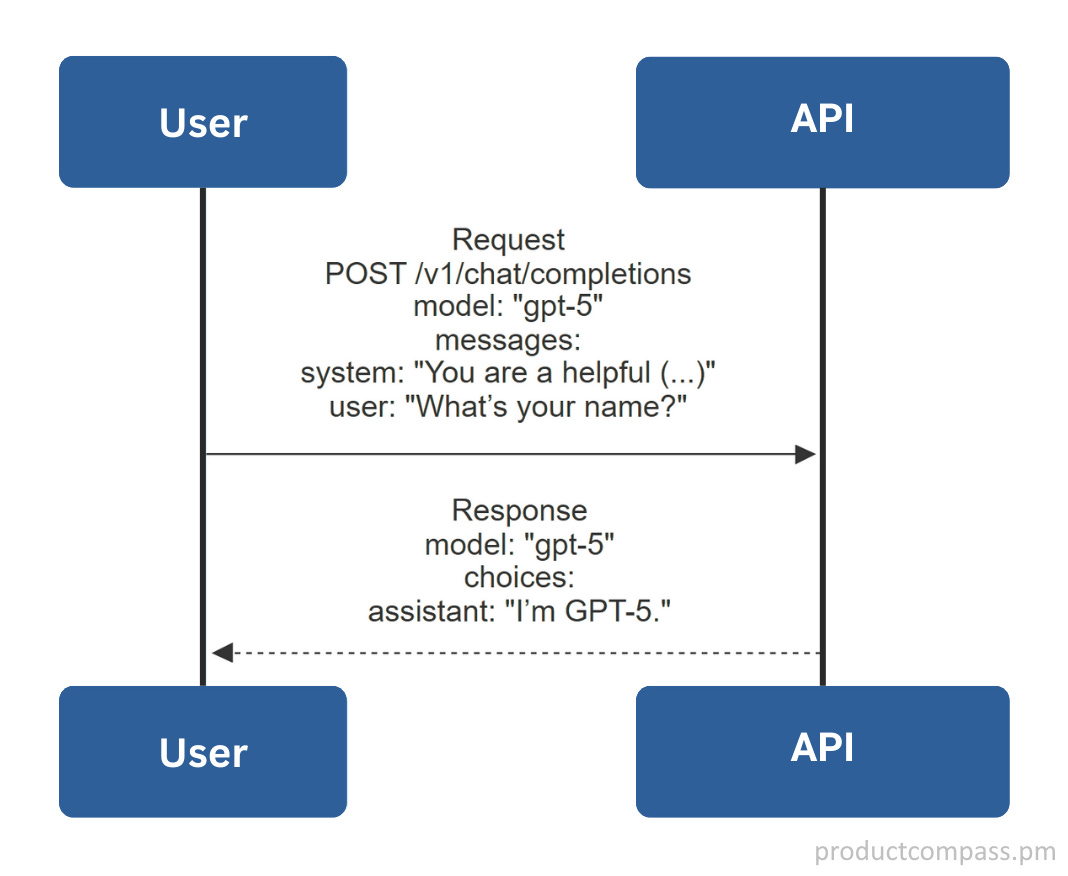
Option 1: Chat Completions API
This is the industry baseline. It’s used by virtually all commercial LLM agents, coding agents, and by default in all agentic frameworks such as n8n, LangChain, LangGraph.
Each our requests defines the model, a list of messages (e.g., user, system, developer, tool) and optional parameters (stream, tools, max_tokens, temperature, etc.). The LLM replies and includes extra information about consumed tokens (skipped below).
A high-level diagram:
You can test it with different models using OpenRouter. That’s the cheapest way to compare different LLMs without multiple subscriptions or hosting models yourself.
Short demo (I ran a prompt to compare three LLMs):
We can later see detailed logs in OpenRouter (note how cheap my requests were):
Things to keep in mind:
Chat Completions API is stateless: if you want memory, you resend the last few turns yourself (chatbots do it by default).
It’s portable across vendors (Google, Anthropic, xAI, DeepSeek, etc.).
You can use solutions like OpenRouter as proxies for vendor/model selection.
You can add custom tools via JSON schema, but not OpenAI’s built-in tools like Web Search or Code Interpreter.
This is the simplest LLM API we discuss in this post. At the same time, to set realistic expectations, many product teams working with LLMs prefer Chat Completions API. They add extra features (memory, tool use, MCP) without relying on vendors. Many of those features are offered by agentic frameworks.
Detailed documentation of the API: Chat Completions by OpenAI
Option 2: OpenAI Assistants
Assistants are “pre-configured AIs” with instructions, models, and built-in tools.
You can configure and test them directly in the OpenAI Platform > Assistants (requires a credit card, but you pay only for the tokens you consume; it’s symbolic, especially if you use 4.1-mini or 4o-mini models).
A quick demo. I created a new Recipe Assistant and uploaded 5 PDFs with recipes:
Assistants API v1 (legacy)
The first version. Deprecated, will shut down Aug 26, 2026.
More: OpenAI Assistants Migration Guide
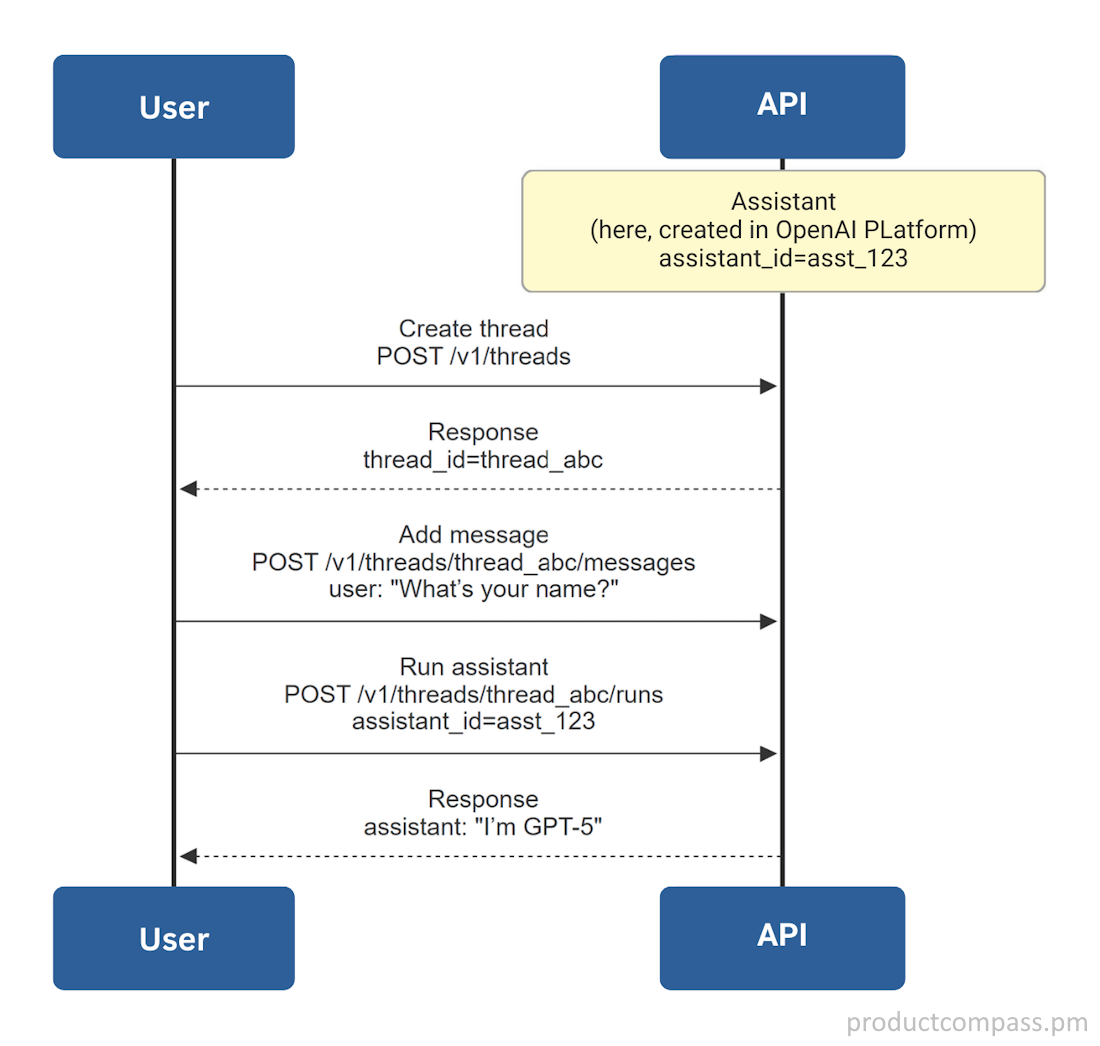
Assistants API v2 (will be shut down on Aug 26, 2026)
The current way to run assistants with memory + built-in tools (RAG, Code Interpreter, file handling). All requests need the OpenAI-Beta: assistants=v2 header.
A high-level diagram:
OpenAI doesn’t promote Threads API, but that might be the easiest way for you to build a real RAG chatbot with truly persistent threads.
This might be great for prototyping, but it will also shut down on Aug 26, 2026. More:
Option 3: OpenAI Prompts + Responses API
The Responses API is the new standard for calling models or prompts.
While stateless, you can get multi-turn conversations (and even conversations with branches) by providing the ID of the previous response in API calls.
For many use cases, you want to combine Responses API with prompts. Prompts are reusable, versioned templates. They can include variables and tools: File Search (retrieval), Code Interpreter, MCP, Web Search, and Image Generation.
You can configure Prompts directly in the OpenAI Platform > Chat.
A quick, simple demo. I created a new Healthy Recipes prompt without any predefined messages and uploaded 5 PDFs with recipes:
A high-level diagram:
Things to keep in mind:
After saving a prompt, you can use prompt_id + version in Responses API calls. This gives you a full prompt versioning and control over how prompt versions are deployed.
Those “conversation threads” do not persist long-term. Most sources say around 30 days. So for persistent threads, you still might want to use Threads API or build a custom database.
More: Responses guide (OpenAI)
LLM APIs Comparison
A brief overview of the available options:
TLDR; Other AI APIs
As the primary focus was on LLMs, I didn’t include OpenAI’s:
Images API: Create new images from text prompts, can use a mask.
Video API: A new API for text-to-video generation
Audio API: They can convert speech-to-text, text-to-speech. Baked in Responses API, but also available as standalone endpoints.
And many others, such as:
Image APIs: Stability AI API, Google Imagen in Vertex AI
Video APIs: Runway, Google Veo
Audio APIs: ElevenLabs, AssemblyAI
We’ll discuss some of them when building AI agents.
Exercise 1: Build a Simple Chatbot: Lovable and Chat Completions API
You will learn:
Starting with Lovable
Building a simple chatbot with Chat Completions API, no backend
Step-by-step video
Timestamps:
(00:00-05:50) Building a Chatbot
(05:50-17:24) Debugging how it handles message history to avoid hitting context window limits. I left it to demonstrate a real process. Might not be needed for simple demos.
My initial prompt
Build a simple chatbot using the Completions API. Do not stream responses. It’s a healthy recipe chatbot that helps users plan meals. Do not create any backend. Ask the user for their API key instead.
Example: Build a Chatbot That Can Search PDFs: Lovable and Threads API
I will demonstrate:
Creating a simple backend in Lovable to store secrets
Building a chatbot with File Search and Threads API (using an OpenAI Assistant)
Streaming the responses
Step-by-step video
Timestamps:
(00:00-07:20) Phase 1: Without streaming
(07:20-25:35) Phase 2: With streaming, optional
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to The Product Compass to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.